Types of Due Diligence – Explained

The process of due diligence is integral to numerous corporate transactions, investments, and legal proceedings in order to evaluate risks, possibilities, and compliance requirements. It entails carrying out in-depth investigations, assessments, and analyses of pertinent data and documents. The identification and analysis of various due diligence practices is a crucial component of due diligence. These categories act as focused areas to ensure a thorough evaluation of all relevant business or legal matters.
The main types of due diligence that are frequently used in various contexts will be discussed in this article, along with an overview of their objectives and importance in promoting well-informed decision-making and risk management. An understanding of these categories or types can help professionals and organizations perform due diligence and mitigate potential risks in their endeavors.
Explore With SignalX Due Diligence
1. Financial Due Diligence
In the modern world, financial due diligence is among the most significant. Firms should be aware of the risks, stability, and financial facts before moving through with any transaction. In order to ensure the accuracy of all the financial records included in the confidential information memorandum (CIM), financial due diligence is conducted thoroughly. In a financial audit, for instance, financial accounts, business forecasts, and projections might be taken into account.
When performing financial due diligence, inventory schedules are also crucial to take into account. Today, financial due diligence is arguably the most popular type of due diligence activity to combat business risk.
2. Legal Due Diligence
A critical component of the total due diligence process, particularly when it comes to procurement, is legal due diligence. It tries to discover and evaluate any legal risks connected to the target business or industry being acquired. Legal due diligence covers a range of topics, including contract compliance, litigation risk, and intellectual property rights, and many others.
Compliance with rules and regulations(from Government) is one of the main areas that legal due diligence concentrates on. To make sure that the target company has complied with all relevant national and international legislation in its activities, this type of due diligence entails analyzing all pertinent papers. Failure to comply could expose the acquiring business to hefty liabilities.
The following documents are routinely examined and reviewed as part of legal due diligence:
- Minutes of Board meetings over the previous three years
- Copy of Memorandum of Association
- Copy of Articles of Association
- Copies of partnership and license agreements and share certificates
3. Tax Due Diligence
Tax due diligence is a thorough investigation of all potential taxes that may be levied against a specific business as well as all taxing jurisdictions that may have a sufficient link to make it liable for such taxes.
Tax due diligence is a process primarily utilized by buyers in a transaction to pinpoint any substantial tax liabilities that could pose a risk. Unlike the preparation of annual income tax returns, which might focus on minor discrepancies or errors (for instance, whether a disallowed meal and entertainment deduction should have been $10,000 instead of $5,000), tax due diligence is more concerned with larger financial figures.
These figures are ones that could potentially sway a buyer’s negotiation stance or decision to go ahead with a transaction. The threshold for what is considered significant in this context can vary, depending on the overall value of the deal or the objective if the contract only pertains to a part of the stock.
4. Operational Due Diligence
The focus of operational due diligence should be on the company’s operations. This procedure seeks to find every issue currently affecting the business’s operations. Such inquiries might put more of an emphasis on assets, technology, and existing infrastructure.
The aim of carrying out an operational due diligence should be to find any hidden dangers in a company’s operations. Operational due diligence also concentrates on identifying potential liabilities in the business’s operations.
5. Intellectual Property Due Diligence
Intellectual property encompasses any non-physical asset that is legally safeguarded and belongs to a person or a business, such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets. It’s crucial for nearly all businesses to possess intellectual property for their growth or revenue generation.
Carrying out due diligence on intellectual property can augment the worth of these assets. Consequently, the primary goal of due diligence is to evaluate the potential risks in a transaction between the buyer or investor and the seller.
6. Commercial Due Diligence
The process through which a buyer examines a potential company from a commercial standpoint is known as commercial due diligence. Commercial due diligence aims to give the buyer a comprehensive understanding of the company based on its position in its market or markets and how that is likely to change in the years to come.
7. Information Technology Due Diligence
The investigation of an organization’s technology products, architecture, and processes is known as technology due diligence, often known as IT or technical due diligence. Technology due diligence, is assessing a company’s IT procedures and infrastructure (sometimes with a focus on security assessment).
Technology due diligence is performed with security assessment in mind. With the rising trends in cybersecurity attacks and data security breaches, IT Due diligence makes a crucial type of due diligence. IT due diligence is carried out from both side parties(sell side and buy side).
The evaluation process in an IT due diligence covers aspects such as technical debt, software licensing, open source components, technical risks, cybersecurity testing and compliance, data management and protection, system architecture, technology budgets and spending, and onboarding.
8. Human Resource Due Diligence
Due diligence in human resources is a crucial procedure for any firm. This type of due diligence concentrates on the employee(a company’s most valuable asset). As a result, when doing due diligence on a company’s human resources, its organizational structure should be taken into account.
The salary and perks built into the business’s structure are the other major points of emphasis in this situation. The examination may also pay close attention to any current collective bargaining agreements that exist between a corporation and other unions.
Human resource due diligence also takes into account any current harassment and unfair dismissals inside a corporation. When completing human resources due diligence, such elements that could have negative legal repercussions for a company should be at the top of the list.
9. Regulatory Due Diligence
A regulatory compliance audit of a corporation, its projects, and its staff is known as regulatory due diligence. The goal of regulatory due diligence in any business transaction environment is meant to make sure that a target firm doesn’t have any regulatory inconsistencies and is not exposed to any litigation due to non compliance with the regulations.
As a business grows and diversifies its activities and geographic reach, it must cope with an expanding number of legal settings, raising the possibility of discrepancies. A regulatory due diligence not only evaluates the compliance status of the target company but also assesses the compliance status of its suppliers, vendors, agents and partners.
10. Environmental Due Diligence
Every business engages in some sort of interaction with the outside world. Therefore, environmental due diligence aims to ensure that these businesses carry out the external due diligence process within the parameters of the established environmental control standards.
The organization’s facilities, operations, and equipment are just a few of the usual areas of focus during environmental due diligence. Additionally, it is important to determine whether any environmental protection laws have been broken by the company, especially to evaluate adherence to the ESG compliance regulations . The main goal of this type of due diligence is to eliminate the potential for fines, which are currently levied or might be in the near future which may occur due to non compliance with the environmental laws.
Environmental due diligence also entails running an evaluation on the properties like land or factories owned by the company for possible environmental contamination risks, such as groundwater or soil contamination, pollution of water bodies with industrial waste & chemicals.
11. Confirmatory Due Diligence
Once a letter of intent or term sheet has been released, the confirmatory due diligence process is usually started. Its goal is to verify all presumptions that purchasers may have regarding the object of their acquisition. Confirmatory due diligence is best conceived of as a stage in the due diligence process because it includes several different forms of due diligence.
12. Customer Due Diligence
Customer due diligence (CDD) is the process of gathering personal data to confirm a client’s identification and more precisely determine the degree of risk they pose.
A customer’s name, address, information about the business they are involved in, and plans to utilize their account are the three essential pieces of information that CDD mandates businesses to acquire. Companies should then check the collected information against official documents like driver’s licenses, passports, utility bills, and incorporation paperwork in order to make sure that clients are being truthful.
13. Asset Due Diligence
Asset due diligence is another type of due diligence performed in a business transaction. A thorough schedule of fixed assets and their locations, all equipment lease agreements, a schedule of sales and purchases of significant capital equipment over the previous three to five years, real estate deeds, mortgages, title insurance, and use permits are typically included in asset due diligence reports.
It is highly recommended for companies to perform physical verification of these assets before making any transactions.
14. Administrative Due Diligence
An administrative due diligence entails verifying administrative-related elements such as facilities, occupancy rates, the number of workstations, etc. The goal of this type of due diligence is to confirm the numerous properties that the target company owns or occupies and to ascertain whether all operational expenditures are included in the financials or not.
Admin DD also gives a better picture of the kind of operational cost the buyer is likely to incur if they plan to pursue expansion of the target company.
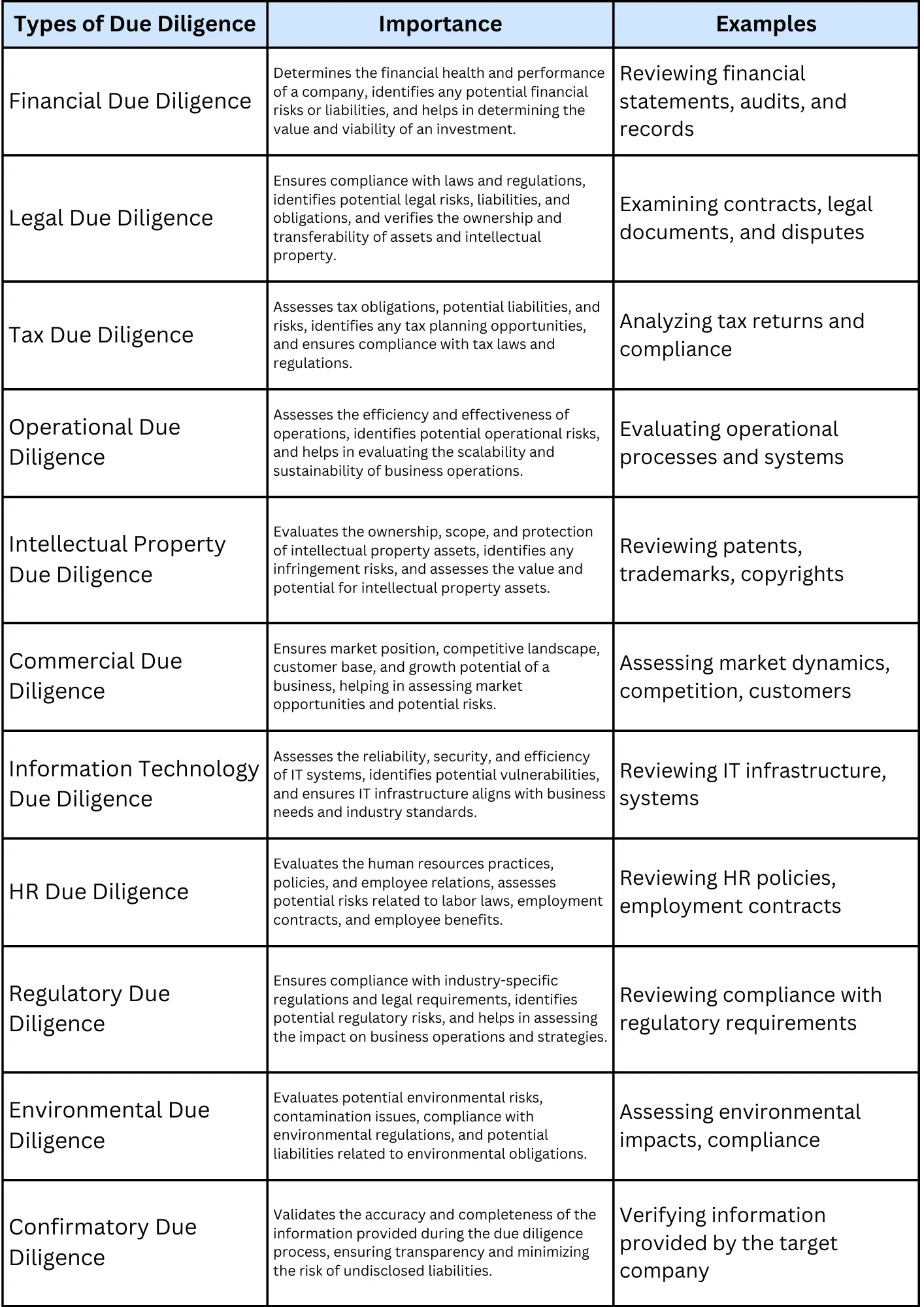
Summary of Different Types of Due Diligence
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the objective of due diligence?
Due Diligence is performed in order to verify and validate the legitimacy of a target entity before entering into a financial transaction. There are several use cases of due diligence, for example, M&A deals, investment deals, vendor onboarding, customer onboarding, etc.
No matter the use case, the objective of any due diligence activity is to perform, risk assessment to identify and evaluate risk associated with the target entity, background verification to validate the legitimacy of the target’s assets, financial records and intellectual property ownership , compliance check to make sure the target entity is compliant with government regulations.
Q2: What is a Due Diligence Checklist?
A Due Diligence Checklist is a list of items or checks that need to be executed on the target entity before entering into a financial transaction or agreement. This checklist helps to build a complete profile of the target entity and also helps to identify and mitigate risks beforehand.
Some of the key checks that a due diligence checklist mainly consists of are –
- Corporate Structure and Governance
- Financial Statements
- Contracts and Agreements
- Intellectual property
- Regulatory Compliance
- Litigation and legal data
Q3: What are the three types of Due Diligence?
The above article already discussed 14 major types of due diligence. To jot down 3 major types among the above list then that will be –
Financial Due Diligence: Evaluate the financial health of a target company. It involves examination of financial statements, tax returns and filings, audit reports, and other financial data.
Legal Due Diligence: Evaluates all legal aspects of the target company. That includes, examining contacts, intellectual property rights, pending lawsuits and litigation cases and many more.
Operational Due Diligence – Evaluates the operational standing and capabilities of the company. It reviews the business model, organizational structure, operational processes, supply chain operations, etc.




