In the complex world of finance and business, the term “anti-money laundering” has gained significant importance.
Today’s business environment makes it very crucial for companies & individuals to understand the concept of money laundering and the importance of anti-money laundering measures in order to stay compliant and counter financial crime and terrorism.
This article will guide you through a comprehensive journey of understanding what Money Laundering is and what the concept of anti-money laundering means. You will also explore the anti-money laundering laws in India and the importance of staying compliant with the regulating laws.
What is Money Laundering?
Money laundering is an act or attempted act of concealing or disguising the identity of illegally obtained proceeds(money) so that they appear to have originated from legitimate sources. It is omnipresent and is present in most areas of industries now.
The advent of digital technology and new forms of money such as cryptocurrencies, bitcoins, etc. has aggravated the problems more. This is where anti-money laundering measures come into play.
What is Anti-Money Laundering?
Anti-money laundering refers to a set of laws, regulations, and procedures intended to prevent criminals from disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate income.
These measures are crucial in the fight against serious crimes such as terrorism & terror financing, illegal arms sales, financial crimes, smuggling, and illicit drug trafficking.
Why is Anti-Money Laundering Important?
The importance of anti-money laundering cannot be overstated. It helps maintain the integrity of markets and financial institutions by preventing the kind of illegal activities that can destabilize them.
It also protects businesses from being used as vehicles for money laundering, thereby safeguarding their reputation and ensuring their compliance with regulatory requirements.
Many instances of laundering are done by criminals involved in terrorism, illegal arms sales, financial crimes, smuggling, or illicit drug trafficking. But sometimes the general public also indulges in money laundering to evade taxes and bribe officials.
Associating with a business, a business partner, or joint venture involved in money laundering brings on you serious financial, legal, and reputational risks, and disables you from conducting business with regulated industries in India and with many developed nations, making anti-money laundering measures so crucial.
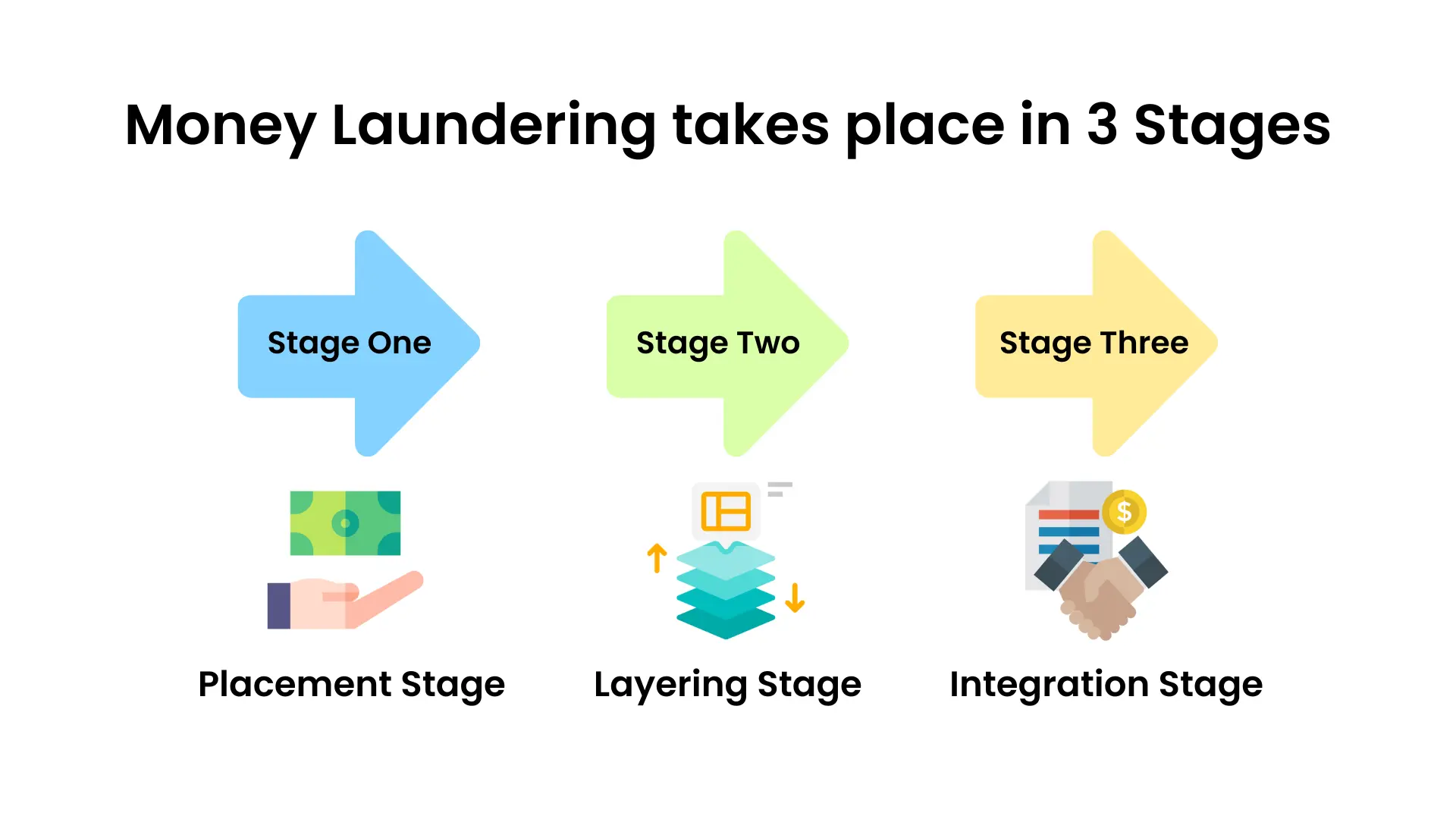
Placement Stage- This is the stage where the launderer segregates a large number of sums into smaller amounts and then deposits them either by cash or by cheques or by money orders. In this case, banks have to be a little cautious and report high-value transactions(if they sense something suspicious). Anti-money laundering regulations play a key role in this stage.
Layering stage – This is the stage where the launderer performs various transactions by making transfers to different bank accounts of family members, friends, relatives, or other persons, to different accounts of other countries. Or by purchasing gold, properties, shares, diamonds, etc.
Integration stage – This stage is the final stage where the money launderer infuses the money back into the system, by purchasing shares, luxury items, and investing in a business, or real estate. During this stage, the launderer easily uses the money without getting caught due to the lack of authentication required.
At present, with technological advancements and AI being the center of the stage it has become much easier for companies and governments to monitor transactions in real time, identify the sources of transactions, and generate red flags on suspicious patterns and behavior.
Anti-Money Laundering Laws in India
There are serious legal and regulatory implications if you knowingly or unknowingly abet money laundering activities. The legislature has made various laws on anti-money laundering to stop the illegal use of money and other criminal activities.
There are many measures taken at the international level to curb this issue as well. Particularly when doing business with global counter-parties, it is a regulatory requirement to execute anti-money laundering compliance due diligence checks. (Especially for companies operating in the Financial and Banking Industry)
There are different treaties and agreements such as:
- The Council of Europe Convention on Laundering, Search, Seizure, and Confiscation of the Proceeds of Crime,
- United Nations Global Programme Against Money Laundering,
- The United Nations Convention against Illicit Trafficking in Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, also known as ‘Vienna Convention’,
- The Financial Action Task Force, etc
These regulations are put in place to assist businesses from all around the world. These international agreements play a crucial role in shaping anti-money laundering laws and regulations all around the world.
Before the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 came into force in India there was other legislation concerning anti-money laundering.
- The Conservation of Foreign Exchange and Prevention of Smuggling Activities Act, 1974, The Benami Transactions (Prohibition) Act, 1988,
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 – the NDPS Act,
- The Indian Penal Code, 1860 and Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973,
- The EC Directive on Prevention of the use of the Financial System for the Purpose of Money Laundering, 1991.
These laws laid the groundwork for the current anti-money laundering framework in India.
The Indian Penal Code, 1860 and The Criminal Procedural Code- It talks about the various criminal activities and the procedures to be followed while punishing the lawbreakers, including the money launderers and those abetting it. These laws are integral to the enforcement of anti-money laundering measures in the country.
Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002- The Act was enacted with a view to prevent money-laundering, the confiscation of assets acquired through it and to deal with issues associated with it. The Act comprises 10 chapters having 75 sections and 1 schedule divided into 5 parts. This Act is the cornerstone of anti-money laundering legislation in India, providing the legal framework for the detection, prosecution, and prevention of money laundering activities.
RBI has issued a Master Circular on Anti-Money Laundering (AML) standards where banks are advised to follow KYC policy for the opening of accounts and monitoring transactions and if found something suspicious reporting it to the appropriate authority. This is a key aspect of anti-money laundering compliance in the banking sector.
Importance of Compliance with Anti-Money Laundering Regulations
Compliance with anti-money laundering regulations, particularly the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) in India, is not just a legal necessity but also a crucial step towards maintaining the integrity of an organization’s operations.
The PMLA regulations in India were established to prevent and control money laundering and provide for confiscation and seizure of property obtained from laundered money.
Companies who are non-compliance with the anti-money laundering regulations can expose themselves to severe penalties, including hefty fines and imprisonment. Moreover, it can damage the reputation of the organization, leading to loss of business and trust among stakeholders. Therefore, it is now imperative for organizations to have robust AML systems in place.
The PMLA regulations in India require organizations to maintain a record of all transactions; the nature and value of such transactions should be recorded if they cross the prescribed limit(this limit varies from account to account). Organizations are also required to furnish information of such transactions to the Financial Intelligence Unit of India (FIU-IND).
In the digital age, with the rise of online transactions, compliance with AML regulations has become even more critical. Digital payment providers, in particular, need to be vigilant about the transactions passing through their platforms. They must ensure that their platforms are not being used to launder money or finance terrorism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the AML KYC process?
The AML (Anti-Money Laundering) KYC (Know Your Customer) process is a set of procedures used by financial institutions to verify and identify customers to prevent financial crimes.
The process involves collecting customer identification information(KYC information), assessing their risk profile, conducting due diligence, and monitoring transactions. It helps companies to comply with regulations, prevent money laundering, and ensure the integrity of the financial system.
What is a red flag in AML?
In Anti-Money Laundering, a red flag is a suspicious indicator that suggests the possibility of money laundering or illicit activities.
It can include unusual transaction patterns, rapid movement of funds, high-risk countries or individuals, inconsistent customer information, unusual business activities, and cash-intensive businesses. Using these red flag indicators companies can perform further investigation and monitoring to detect and prevent financial crimes.
What are the AML Risk Levels?
Anti-money laundering risk levels represent the varying degrees of risk associated with customers, business relationships, or transactions regarding potential involvement in money laundering or financial crimes.
The risk levels can be classified into low, medium, and high. Low-risk customers have minimal risk, medium-risk customers require additional scrutiny, and high-risk customers have a significant potential for involvement in illicit activities.