Risk Based Approach to TPRM: Key Considerations and Benefits

In today’s interconnected business landscape, organizations are relying more on third-party vendors, suppliers, and service providers to meet their operational needs. While outsourcing certain functions can bring numerous benefits, it also introduces various risks that must be effectively managed. Third-party risk management (TPRM) is a crucial discipline that helps organizations mitigate the potential risks associated with their extended enterprise.
To enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of TPRM programs, many organizations are adopting a risk based approach to tprm in order to mitigate risks from third parties. This approach prioritizes resources and efforts by focusing on the risks that pose the greatest potential harm to the business. In this article, we will explore the benefits and key considerations of adopting a risk based approach to TPRM.
Understanding the Risk Based Approach to Third Party Risk Management
A risk based approach to TPRM involves assessing and prioritizing third-party risks based on their potential impact on the organization. It shifts the focus from a one-size-fits-all approach to a more tailored and dynamic methodology. By categorizing and prioritizing risks, organizations can allocate their limited resources more effectively and efficiently.
and protect your organization with smarter third-party risk management.
Benefits of taking a Risk-Based Approach:
Enhanced Risk Visibility:
By adopting a risk-based approach, organizations gain a comprehensive view of their third-party risks. This enables them to identify and understand the most critical risks, allowing for more targeted mitigation strategies.
Resource Optimization:
A risk-based approach allows organizations to allocate their resources in a more efficient manner. By prioritizing high-risk third parties, they can focus their efforts on implementing stronger controls and conducting more rigorous due diligence.
Proactive Risk Management:
A risk-based approach encourages proactive risk management. Organizations can identify potential risks early on, enabling them to implement preventive measures and respond to emerging threats promptly.
Improved Compliance:
Adopting a risk-based approach aligns TPRM programs with regulatory requirements and industry best practices. By addressing the most significant risks, organizations can demonstrate compliance more effectively and mitigate legal and reputational risks.
Key Considerations for Implementing a Risk-Based Approach
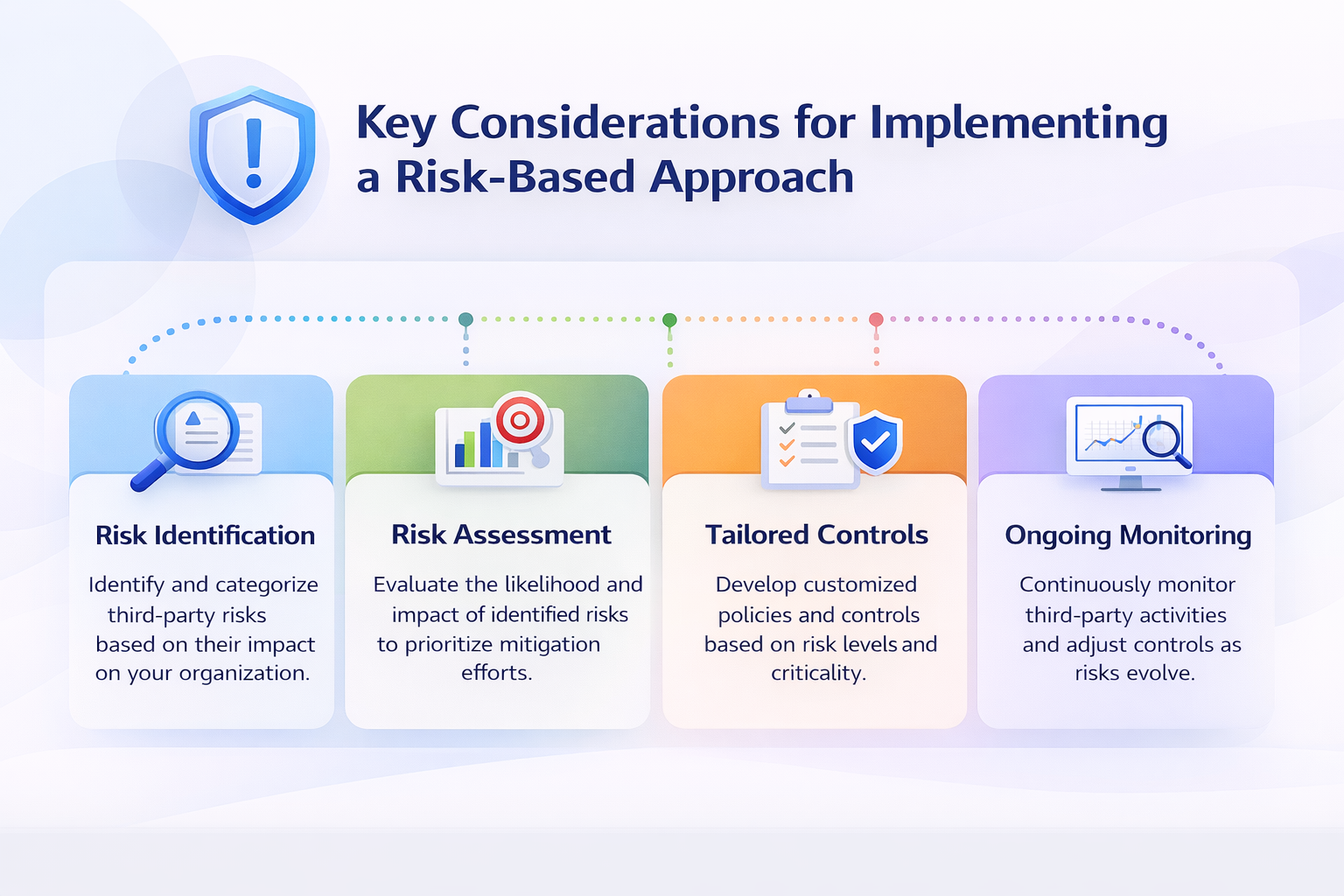
Risk Assessment Methodology:
Organizations must develop a robust risk assessment methodology that aligns with their specific industry, business objectives, and risk appetite. This methodology should consider factors such as inherent risk, control environment, and residual risk to effectively prioritize third-party risks.
Continuous Monitoring:
Implementing a risk-based approach requires ongoing monitoring of third-party relationships. Organizations should establish mechanisms for automated continuous risk assessment and stay updated on changes in the risk landscape.
Communication and Collaboration:
Effective communication and collaboration between internal stakeholders, such as procurement, legal, and IT departments, are crucial for successful TPRM implementation. It ensures a shared understanding of risks and facilitates timely decision-making.
Integration with Vendor Management:
Organizations should integrate the risk-based approach into their broader vendor management framework. This integration allows for a holistic view of third-party risks and ensures consistency in risk evaluation and mitigation across the organization.
reduce compliance burden, and make smarter risk decisions.
Importance of Risk Categorization in Risk based approach to TPRM
A successful risk-based strategy for managing third-party risks necessitates that companies implement a classification system for their third-party entities. This means designating each entity to a particular risk level, such as Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3, which correspond to high, medium, and low-risk categories respectively.
The basis of this tier system is the recognition that different third-parties present diverse levels of risk, depending on several factors like the type of services or goods they offer, their access to confidential data, and their importance to business operations.
The classification into risk tiers offers several advantages. It helps simplify the risk management process by defining the kind and severity of evaluations required for each third-party. Furthermore, it offers a straightforward understanding of where potential dangers may exist and assists in prioritizing risk reduction efforts.
Risk tiers can also direct resource distribution for risk management activities, ensuring that the most crucial third-parties are subjected to the most rigorous scrutiny.
However, the classification process doesn’t apply uniformly to all situations. It demands a collaborative effort, involving the viewpoints of various stakeholders within the organization. For example, a third-party handling large transactions may be seen as high risk from a financial perspective but low risk from a cybersecurity viewpoint.
This cross-departmental collaboration guarantees a more comprehensive and accurate comprehension of third-party risks, ultimately leading to more effective risk management.
To effectively apply this tier system, organizations need to develop a series of checks and evaluations specific to each risk tier. The type and scope of these checks will be determined by the risk level associated with each tier.
Conclusion
Adopting a risk based approach to TPRM enables organizations to prioritize and manage third-party risks more effectively. By focusing efforts on the most significant risks, organizations can optimize resource allocation, enhance risk visibility, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Implementing this approach requires a robust risk assessment methodology, continuous monitoring, effective communication, and integration with vendor management practices. By embracing a risk-based approach, organizations can strengthen their TPRM programs and build resilient relationships with their third-party partners.
