What is Supply Chain Management and why is it important?

What is the definition of supply chain management (SCM)?
Supply chain management or SCM is the management of all processes that facilitate the transformation of raw materials into a business’s final product. This includes all activities from sourcing raw materials and services necessary for the production of value, to delivering the finished product or service to the end customer.
The purpose of Supply Chain Management is to maximize customer value, drive quality, optimize costs, improve efficiency, and thereby the profitability of the business. Effective supply chain management enables businesses to compete in the market and reliably deliver value to customers.
So what does supply chain management involve? Let’s find out.
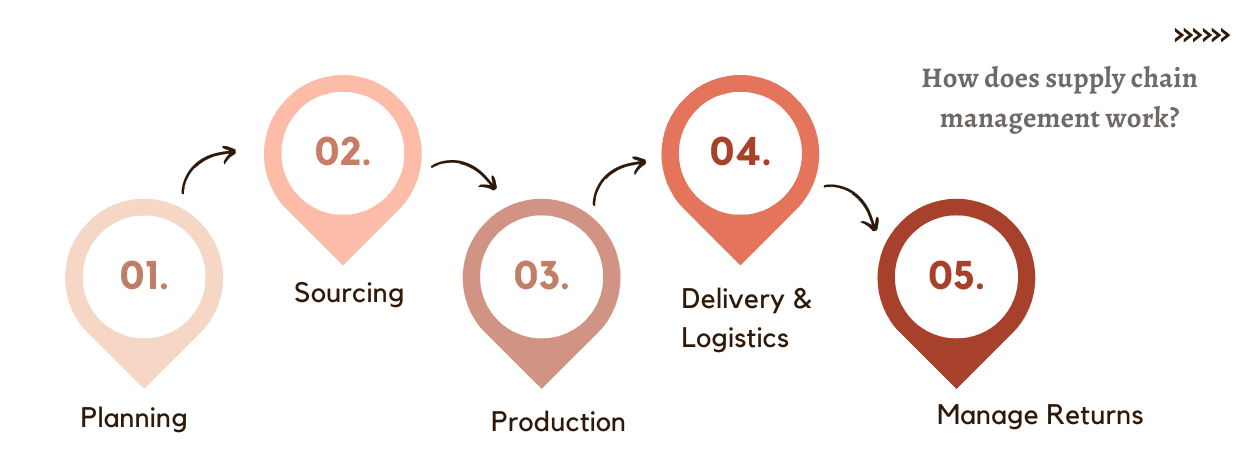
How does supply chain management work?
Traditionally, there are 5 components of SCM. Supply Chain Managers or SCM professionals as they are called are responsible for executing the following functions through a variety of tools and processes.
- Planning: Plan and manage all resources required to produce the value expected by the customers. Implement processes that capture essential performance data of the supply to determine whether the supply chain is efficiently meeting the business goals by delivering the promised value at the promised quality levels to the customers within the cost and profitability expectations of the business. Implement systems that build visibility of operations and efficient movement of materials.
- Sourcing: Choosing suppliers to provide the required services and materials needed to create value for the customer, keeping in mind quality, cost, and compliance expectations is a key part of sourcing in supply chain management. This is then followed by establishing processes to manage supplier relationships, monitor quality of output, supplier due diligence and monitor for third-party risks.
- Production: Execute the activities required to accept raw materials, manufacture the product, test for quality, package for shipping, store and manage inventories and prepare for delivery.
- Delivery and Logistics: Coordinate customer orders, schedule deliveries, dispatch loads, invoice customers and receive payments.
- Manage Returns: Implement and manage processes to take back defective pieces, request refunds, and manage recalls.
Why is supply chain management important?
Effective supply chain management systems minimize cost, waste, and time in the production cycle. The industry standard has become a just-in-time supply chain where retail sales automatically signal replenishment orders to manufacturers. Retail shelves can then be restocked almost as quickly as the product is sold. One way to further improve this process is to analyze the data from supply chain partners to see where further improvements can be made.
Effective Supply Chain Management drives Profits, Quality, and Efficiency in any business.
- Profit Driver: Modern-day supply chain management identifies scope for automation, applies AI to predict demand and supply, and optimizes inventory movement to ensure the promised inventory is available and delivered reliably to the customer, be it an internal customer or an external customer.
- Quality and Customer Experience Driver: Effective Supply Chain Management keeps the quality of product, reliability of delivery, and efficiency of operations at its heart. Today’s supply chains produce 50 times more data than the networks 5 years ago. Making use of this data to improve product quality, source from reliable suppliers, identify developing risks at the supplier end, manage risk to avoid disruptions, etc. are key responsibilities of supply chain management professionals today. This is vastly different from the earlier expectations of cost management and inventory keeping.
- Efficiency Driver: Ever since Henry Ford commercialized the assembly line, and ever since globalisations swept across supply chains and transformed systems from being vertically integrated to being interconnected with third parties, efficiency has been at the forefront of business expectations from supply chains. AI, automation, robotics, and other such technologies are pushing supply chain management into its new era.
The question is not if supply chain management is dying, but it is what the future is going to look like and what expectations will we have of supply chain management, and what skills professionals need to inculcate to excel in modern supply chain management. Let us find out.
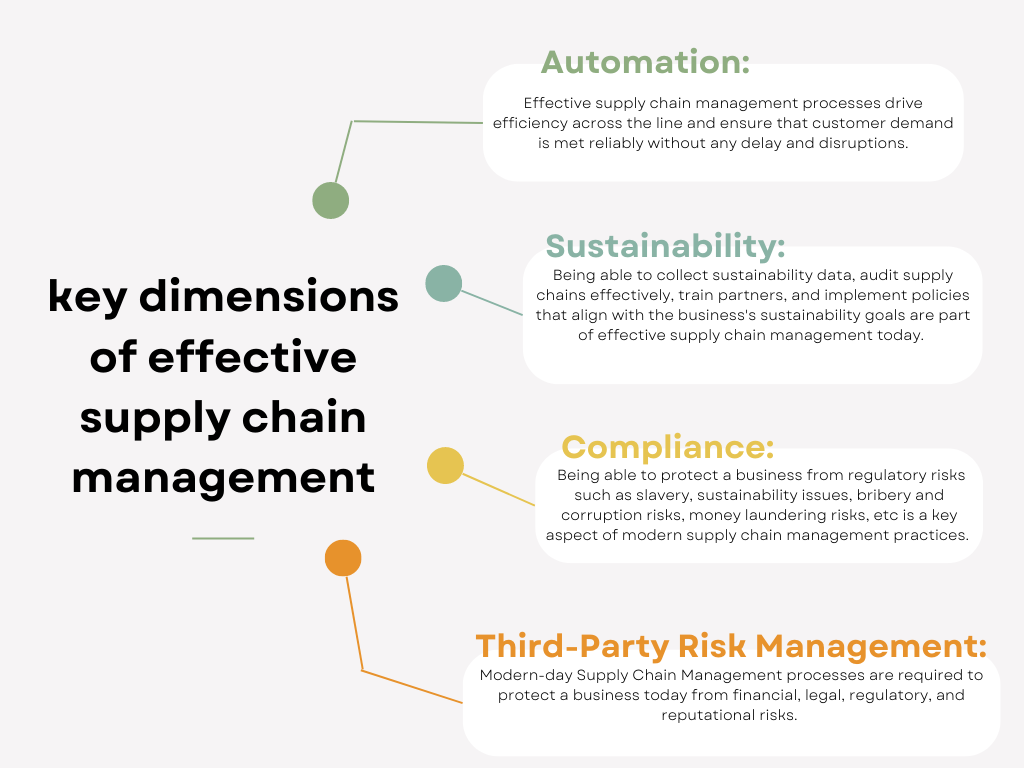
What are the key dimensions of effective supply chain management?
The more effective a company’s supply chain management is, the better it can deliver quality products and services to its customers reliably and cost-effectively. An effective and resilient Supply Chain is the backbone of any modern business. As new technologies enter the market, supply chain management practices are also required to transform to ensure that the business can effectively compete and deliver value in the market. Today’s supply chains look very different from the ones 10 years ago, and today’s supply chain managers are required to perform tasks that were not in the traditional textbooks. So what does a modern supply chain management practice entail?
Supply chain management today is expected to transform the business into the Industry 4.0 era. This comes with a set of 4 key aspects of supply chain planning that influence the quality, customer experience, efficiency, and profitability of any business. Supply Chain Managers or SCM professionals are expected to facilitate the following to keep up with the changing times:
- Automation: Modern supply chain management today has automation at its core. Effective supply chain management processes drive efficiency across the line and ensure that customer demand is met reliably without any delay and disruptions. As we transition into Industry 4.0, supply chains are at the cusp of transformation again. Technologies such as AI, Robotics, Big Data Automation, IoT, Virtual Reality, etc are promising a paradigm shift in productivity and efficiency of operations. These are tools now available for supply chain teams to leverage to further drive automation possibilities
- Sustainability: 98% of ESG risks that businesses carry today emerge from their supply chains. There are increasing incidents of businesses suffering reputational damage and facing the wrath of customers and regulators for inviting ESG risks into their production lines. This could even come from a minuscule supplier in the extended supply chain mismanaging hazardous waste, or employing slavery. Being able to collect sustainability data, audit supply chains effectively, train partners, and implement policies that align with the business’s sustainability goals are part of effective supply chain management today.
- Compliance: Legislations such as FCPA, UKBA, and other anti-corruption laws state that customers can, under certain circumstances, be held liable for the corrupt acts that their suppliers commit on their behalf, irrespective of whether or not the customer was aware of the supplier’s conduct. Sanctions by major governments on each other due to geopolitical conflicts, war, etc affect global supply chains on a near real-time basis and can throw operations haywire making it difficult for supply chain managers to reliably deliver. Being able to protect a business from regulatory risks such as slavery, sustainability issues, bribery and corruption risks, money laundering risks, etc is a key aspect of modern supply chain management practices.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Supply Chain Management teams must protect the business from cyber-intrusions and hacks, risks such as bribery, corruption, modern slavery, fraud, and much more. Modern-day Supply Chain Management processes are required to protect a business today from financial, legal, regulatory, and reputational risks.
Will Supply Chain Management be automated?
Supply Chain Management is of strategic importance for businesses to compete and win in the markets today. Long gone are times, when supply chain management was only about managing the movement of goods and services, today supply chain managers, are responsible for managing data, controlling third-party risks, driving improvements in efficiency through automation and managing effective compliance processes, ensuring business alignment with sustainability goals and much more.
So what is SCM’s future?
Today robotics is playing a key role in driving efficiency across warehouses and fulfillment centers. AI-based systems are distributing products and materials to optimize fulfillment time and delivery operations. As a supply chain manager, today it is more important than ever to be apprised of the latest technologies available in the market that can be leveraged to drive customer experience and profitability. Mundane repetitive tasks are bound to get automated and executed by machines. The opportunity today is for supply chain managers to upskill to play a strategic role in business transformation.
Compliance is another foundational aspect of supply chain management. The penalty for doing business with a compromised supply chain partner is steep today. Businesses are exposed to financial, legal, compliance, and reputational risks due to compromised partners. Risks can appear in various forms – be it a supplier from geography that has been sanctioned or a supplier who is a politically exposed party inviting the risk of bribery and corruption. Regulations such as FCPA, UKBA, and others do not spare businesses from not being aware of bribery, slavery, and corruption risks in their supply chains. Therefore it becomes the supply chain management team’s responsibility to ensure that onboarded partners are meeting the expectations of the business.
Sustainability is another major focus area in modern supply chains, the mandate for which falls on SCM teams at many organizations. It is known that 98% of ESG risks for a business today emerge from its supply chains. Meeting sustainability expectations of customers and investors requires modern supply chain management systems to incorporate ESG risk assessments in their supplier selection process.
Ultimately effective supply chain management in today’s world is essential in delivering quality products and services, meeting customer expectations, mitigating third-party risks, ensuring compliance, managing costs, and driving profitability. As you can see, the scope has well expanded beyond overseeing fulfillment or purchasing.


