Venture Capital Due Diligence: The Complete Framework Modern Investors Use to Win Deals

Venture capital returns are not driven by access alone; they are driven by judgment. The difference between a breakout fund and an average one often comes down to how well investors separate signals from noise during due diligence. In a market where founders are increasingly sophisticated and competition for deals is fierce, surface-level analysis is no longer enough.
Modern venture capital due diligence has shifted from intuition-heavy decision making to a more structured, data-driven discipline. Today’s top firms combine pattern recognition with analytics, qualitative insights with hard metrics, and speed with rigor. This evolution is not optional. Funds that fail to adapt risk overpaying for hype while missing genuinely defensible businesses.
In this guide, you’ll learn how venture capital due diligence really works in practice. We’ll break down a step-by-step framework, explore each diligence type in depth, highlight common red flags, and share how elite firms build repeatable diligence systems that consistently outperform.
What is Venture Capital Due Diligence?
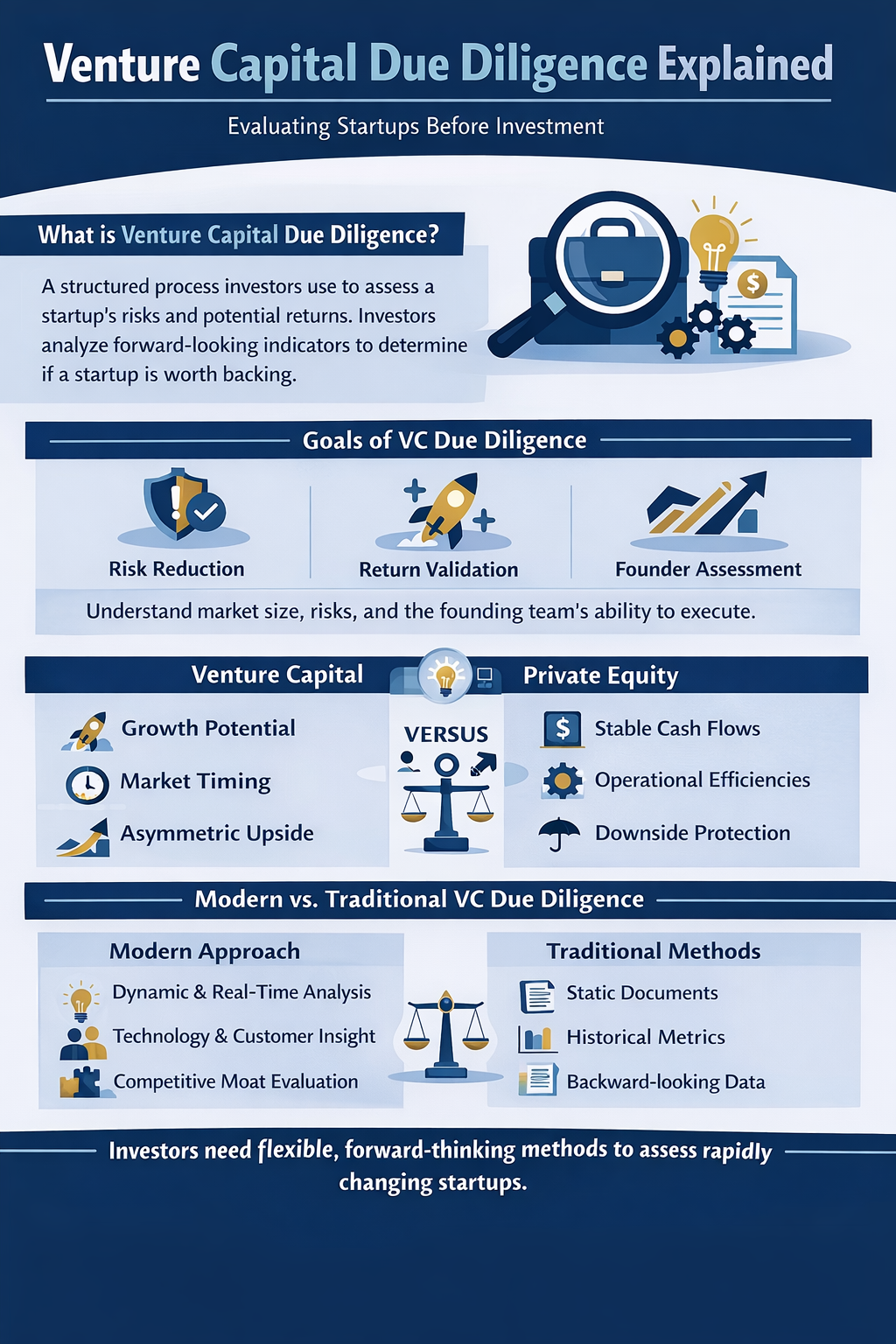
Venture capital due diligence is the structured process investors use to evaluate whether a start-up is worth backing. From an investor’s perspective, it is not about proving a company is perfect, but about understanding where the risks lie and whether the potential return justifies those risks.
The primary goals of VC due diligence are risk reduction, return validation, and founder assessment. Investors want confidence that the opportunity is real, the market is large enough to produce venture-scale outcomes, and the founding team can execute under pressure. Unlike later-stage investing, diligence in venture capital often focuses on forward-looking indicators rather than historical performance.
VC due diligence differs significantly from private equity diligence. Private equity emphasizes stable cash flows, operational efficiencies, and downside protection. Venture capital, by contrast, prioritizes growth potential, market timing, and asymmetric upside. Because startups operate with limited data, VC diligence must be both flexible and probabilistic.
Traditional diligence methods are becoming outdated because they rely too heavily on static documents and backward-looking metrics. In fast-moving markets, investors now need dynamic analysis, real-time data, and deeper insight into technology, customer behavior, and competitive moats.
When Does Due Diligence Start in the VC Deal Flow?
Due diligence begins far earlier than most founders realize. The process typically starts during pre-screening, long before a formal data room is shared. At this stage, investors assess high-level signals such as founder background, market narrative, and early traction.
Pitch decks play a critical role in early filtering. They shape first impressions and determine whether a deal advances to deeper diligence. However, a compelling deck is only an entry point, not proof of quality.
As a deal progresses, expectations rise. By the time an opportunity reaches an investment committee, partners expect clear answers on risks, assumptions, and upside drivers. Timelines vary by stage, but pre-seed diligence may take days, seed rounds often take two to four weeks, and Series A or later rounds can extend beyond six weeks due to increased complexity.
Types of Venture Capital Due Diligence

a. Financial Due Diligence
Financial diligence focuses on understanding how a startup makes money today and how it plans to do so at scale. Investors look beyond top-line growth to assess revenue quality, distinguishing sustainable revenue from vanity metrics that inflate traction.
Unit economics are central to this analysis. Metrics such as LTV to CAC, gross margins, and payback periods reveal whether growth creates or destroys value. Burn multiple analysis helps investors understand capital efficiency, while scenario modeling tests how the business performs under downside conditions.
b. Commercial / Market Due Diligence
Market diligence validates whether a real and growing demand exists. Investors examine TAM, SAM, and SOM to assess whether the opportunity can support venture-scale returns, but they also challenge overly optimistic assumptions.
Customer interviews and usage data provide insight into buying behavior and pain points. Competitive analysis helps identify whether the company has a defensible position or is vulnerable to incumbents and fast followers. Pricing power is evaluated to determine long-term margin potential.
c. Product & Technology Due Diligence
Product and technology diligence has become increasingly important, especially in software and AI-driven startups. Investors assess whether the product actually solves the stated problem and whether the technology can scale without breaking.
Code quality, infrastructure choices, and tech debt all influence future execution risk. In AI-first companies, defensibility is scrutinized closely, including data advantages, model differentiation, and barriers to replication. Cybersecurity posture is also evaluated, as early weaknesses can become catastrophic at scale.
d. Founder & Team Due Diligence
The founding team remains one of the strongest predictors of success. Investors assess founder-market fit by examining whether the team has unique insight into the problem they are solving.
Execution history matters more than pedigree alone. Investors look for resilience, adaptability, and the ability to make hard decisions. Reference checks provide unfiltered perspectives on leadership style, integrity, and how founders behave when things go wrong.
e. Legal & Compliance Due Diligence
Legal diligence ensures there are no hidden structural risks. A clean cap table is essential, as misaligned incentives or unresolved ownership issues can derail future rounds.
Investors review shareholder agreements, IP ownership, and employment contracts to ensure the company truly owns what it claims. Regulatory exposure is assessed, particularly in fintech, healthtech, and other heavily regulated sectors.
f. ESG & Reputation Due Diligence
ESG and reputation diligence is an emerging but increasingly important area. Investors evaluate ethical risks, governance practices, and public perception, recognizing that reputational damage can quickly destroy value.
Sustainability signals, while not always revenue drivers today, can influence long-term resilience and attractiveness to future investors and acquirers.
The Venture Capital Due Diligence Framework (Step-by-Step)
A structured diligence framework helps investors move quickly without sacrificing quality. The process typically begins with deal sourcing insights that provide context before formal analysis starts.
Initial screening applies a consistent checklist to filter opportunities efficiently. Deep-dive analysis follows, covering financials, market, product, and team. Partner review introduces diverse perspectives and challenges assumptions. Insights are synthesized into an investment memo, which culminates in a final risk scoring and decision.
A repeatable diligence playbook ensures consistency across deals and reduces bias, allowing firms to scale decision-making without diluting quality.
The Ultimate VC Due Diligence Checklist
An effective diligence checklist acts as both a guide and a safeguard. It ensures that market validation is grounded in evidence, financial health is understood, and founder credibility is verified. Product differentiation must be clear, legal risks minimized, and exit potential realistically assessed. The goal is not to eliminate risk, but to understand it fully.
Red Flags Investors Should Never Ignore
Certain warning signs consistently correlate with poor outcomes. Inconsistent metrics across documents suggest either poor controls or intentional misrepresentation. Founder conflicts or unclear decision authority can stall execution.
Overstated market size often masks weak positioning, while low retention signals product-market misfit. Heavy dependence on a single customer increases fragility, and rapid, unexplained pivots may indicate a lack of strategic clarity.
Data-Driven Due Diligence: The Future of VC
The future of venture capital diligence is increasingly data-driven. Investors are integrating alternative data sources, from hiring trends to product usage signals, to gain earlier and more objective insights.
Predictive analytics help identify patterns linked to success or failure, while AI-powered tools flag anomalies and risks that humans might miss. Real-time market intelligence allows investors to track changes even after a deal closes, transforming diligence from a one-time event into a continuous process.
Due Diligence by Funding Stage
Diligence priorities evolve as companies mature. At the pre-seed stage, vision and founder insight outweigh metrics. Seed-stage diligence emphasizes early traction and validation. Series A diligence focuses on scalability and repeatability, while growth-stage diligence scrutinizes unit economics, operational efficiency, and the path to profitability.
Biggest Challenges in Venture Capital Due Diligence
Venture investors operate under persistent information asymmetry, relying on incomplete data and founder narratives. Cognitive biases can distort judgment, particularly when deals move quickly.
The tension between speed and accuracy is constant, and competitive pressure often fuels fear-based decisions. Managing these challenges requires discipline, structure, and a willingness to walk away.
Best Practices Used by Top Venture Capital Firms
Top firms rely on pattern recognition informed by data, not gut feel alone. They conduct independent research to validate founder claims and leverage expert networks for specialized insight.
Customer calls are treated as core diligence inputs, not optional extras. Reverse due diligence, where firms assess how founders evaluate investors, also provides valuable signals about founder maturity and alignment.
Tools That Streamline VC Due Diligence
Technology plays a growing role in diligence efficiency. Market intelligence platforms surface competitive insights, financial modeling tools stress-test assumptions, and deal flow CRMs centralize information. Automated risk monitoring helps firms stay ahead of emerging issues without adding manual overhead.
Post-Investment Due Diligence (Often Missed by Competitors)
Due diligence should not end at closing. Ongoing performance tracking allows investors to detect issues early. Active governance participation improves decision quality, while early risk alerts inform follow-on investment choices and portfolio support strategies.
How Long Does Venture Capital Due Diligence Take?
The duration of venture capital due diligence can differ widely depending on the startup’s stage, the complexity of its business model, and the investment firm’s internal processes. On average, early-stage deals such as pre-seed or seed rounds may take anywhere from 2 to 4 weeks, as investors typically focus on the founding team, market opportunity, and early traction rather than extensive financial history. In contrast, Series A and later-stage investments often require deeper analysis including financial audits, customer validation, legal reviews, and technology assessments which can extend the process to 4 to 8 weeks or more.
Conclusion
Venture capital due diligence is no longer a box-checking exercise. It is a competitive advantage that separates disciplined investors from reactive ones. Structured frameworks, data-driven insights, and continuous learning define the next generation of successful VC firms. In an increasingly crowded market, intelligence-led diligence will determine who wins.
FAQs
What is venture capital due diligence?
Venture capital due diligence is the evaluation process investors use to assess a startup’s risks, growth potential, and ability to generate venture-scale returns. It includes financial, market, product, team, legal, and strategic analysis before an investment decision is made.
Why is due diligence critical in venture capital investing?
Due diligence helps investors identify hidden risks, validate assumptions, and avoid costly mistakes. Because startups operate with limited historical data, structured diligence improves decision quality and increases the likelihood of successful outcomes.
When does due diligence begin in the VC investment process?
Due diligence often starts during initial deal screening, even before formal meetings occur. Early signals from pitch decks, founder backgrounds, and market narratives influence whether a startup advances to deeper analysis.
How long does venture capital due diligence usually take?
The duration depends on the funding stage. Pre-seed and seed diligence can take a few days to several weeks, while Series A and later-stage diligence may extend to six weeks or more due to increased complexity.
What financial metrics matter most during VC due diligence?
Investors focus on revenue quality, unit economics, burn multiple, gross margins, and cash runway. These metrics help assess capital efficiency and long-term scalability rather than short-term growth alone.



