Risks of Strategic Management: Key Challenges for Business Leaders
Risks of strategic management is the backbone of every successful business, guiding organizations toward their long-term goals. But let’s face it, no plan comes without risks. Even the best strategies can go awry if business leaders aren’t mindful of the potential dangers that lie ahead. In today’s fast-paced business environment, the risks of strategic management have never been more pressing.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at the key risks leaders face when executing strategic plans and explore how you can turn those risks into opportunities.
The Reality of Strategic Management Risks
Risks of strategic management involve making high-stakes decisions based on uncertain information. The risks involved are often multifaceted, stemming from internal and external factors. While you can never eliminate risks entirely, understanding what you’re up against is half the battle.
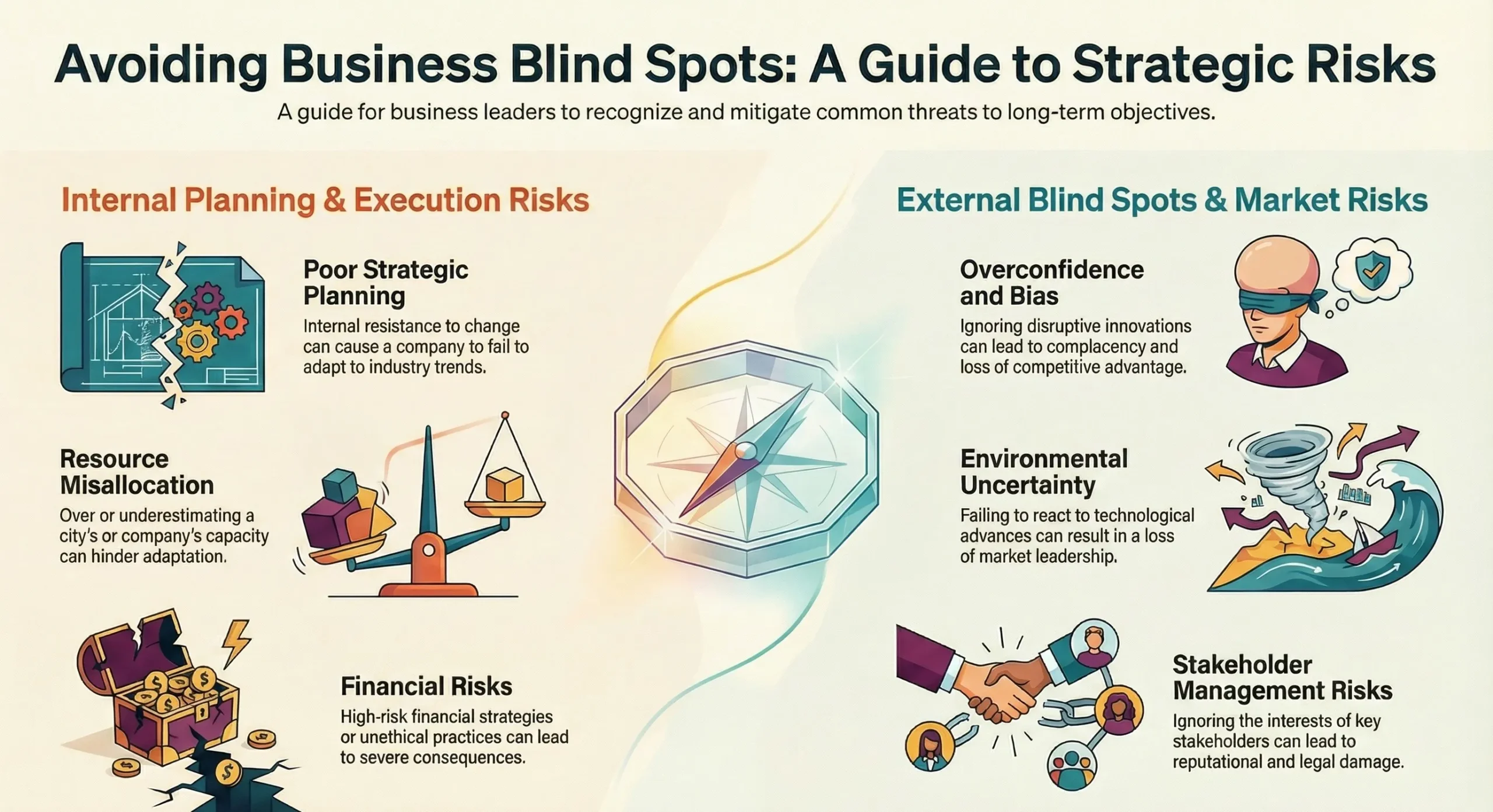
Here are some of the major risks business leaders need to be aware of:
1. Unpredictable Market Conditions
The market is in constant flux. Economic shifts, technological changes, and even global events (pandemics) can quickly render your strategy obsolete.
Risk Factor: A once-strong market can dip without warning, throwing projections off-course. Businesses heavily reliant on certain markets or demographics can feel the sting of these changes.
Mitigation Tip: Diversify your business model and build flexibility into your strategy. Stay agile so you can pivot when market conditions change.
2. Ambiguity in Organizational Vision
What happens when the entire team isn’t on the same page? Chaos, confusion, and poor execution. It’s crucial for leadership to ensure everyone understands the company’s mission and the strategic path to success.
Risk Factor: A lack of clarity leads to wasted resources and missed opportunities, as teams work at cross purposes or fail to prioritize the right objectives.
Mitigation Tip: Regularly communicate your vision and goals. Ensure alignment at every level of the organization to create a unified, forward-focused team.
3. Overlooking Technological Advancements
In the digital age, technological disruptions are a constant threat. The risk here is not just that you might fall behind competitors but that you might miss opportunities to innovate.
Risk Factor: Failing to keep up with new tech trends can cause your company to become irrelevant in a matter of months.
Mitigation Tip: Make technological innovation a part of your culture. Invest in research, foster creativity, and constantly look for ways to leverage emerging technologies.
4. Execution Failures: The Silent Killer
A brilliant strategy is worth nothing if it isn’t executed well. Poor implementation is one of the most common and avoidable risks in strategic management.
Risk Factor: Even with a perfect plan, things can go off track if resources are mismanaged or communication breaks down. Lack of alignment between departments often leads to delays and costly mistakes.
Mitigation Tip: Invest in effective project management, monitor progress closely, and be willing to make adjustments along the way. Don’t just plan do!
5. Internal Resistance to Change
Change is hard. That’s a fact. And even when strategic shifts are necessary, internal resistance can derail efforts. Employees, teams, or even departments may push back if they don’t feel fully on board with the new direction.
Risk Factor: Resistance can lead to stagnation or slow down progress, making it harder to achieve desired outcomes.
Mitigation Tip: Build a culture of change management by involving employees in the strategy formulation process, offering training, and showing the benefits of the changes. Make change feel like a team effort rather than an imposition.
6. Ignoring Competitive Threats
Business is competitive, and being blindsided by a new or existing competitor can quickly undermine your strategy. The biggest risk is assuming that the competition won’t change, or worse, won’t catch up.
Risk Factor: Competition can copy or improve upon your offerings, leaving you scrambling to catch up if you’re not paying attention.
Mitigation Tip: Stay alert. Regularly analyze your competition’s strategies, and be ready to adapt or innovate before they do. Don’t underestimate them.
7. Underestimating the Impact of Global Events
In a globalized world, external events like political instability, trade wars, and even natural disasters can introduce significant risks to your strategy.
Risk Factor: Global disruptions can cause supply chain issues, market volatility, and regulatory challenges that derail your plans.
Mitigation Tip: Stay informed about global trends and risks. Build contingency plans that account for international disruptions, and diversify your operations to minimize exposure.
Turning Risks Into Opportunities
Now that we’ve covered the risks of strategic management, it’s important to remember that these risks are not insurmountable. Every challenge presents an opportunity to grow, innovate, and improve.
- Diversify your risk portfolio: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Whether it’s revenue streams, technology, or market segments, diversify to spread out risk.
- Plan for uncertainty: Prepare your business to be flexible and adapt to unforeseen circumstances. Being reactive rather than proactive can put you behind.
- Foster an innovative culture: Encourage risk-taking within your organization (calculated risks, of course). This allows your company to continuously evolve and stay ahead of the curve.
- Collaborate with experts: Don’t be afraid to seek outside help from industry experts, consultants, or tech partners. They can provide new perspectives that help you avoid risks you might have overlooked.
Here are a few examples that highlight the risks of strategic management in action
1. Environmental Uncertainty
Example: Kodak’s Decline
Kodak was once a dominant player in the photography industry, but it failed to adapt to the rise of digital cameras and smartphones. The company’s strategic risk was ignoring the shift toward digital technology due to a focus on traditional film photography. Kodak’s reluctance to change and embrace the new technological trends ultimately led to its bankruptcy.
Risk: Failing to anticipate or react to environmental changes (technological advancements) can result in a loss of market leadership.
2. Poor Strategic Planning
Example: New Coke
In 1985, Coca-Cola launched “New Coke,” changing the original formula in an attempt to attract younger customers and compete with Pepsi. The change was met with backlash from loyal customers who wanted the original product, leading to a significant loss in market share and consumer trust.
Risk: Poor planning and failing to understand consumer preferences can result in backlash and damage to brand loyalty.
3. Resource Allocation
Example: Tesla’s Cash Flow Crisis (2018)
In 2018, Tesla faced significant financial stress due to its aggressive strategy of ramping up production of the Model 3 electric car. The company overestimated its ability to scale production, leading to cash flow problems and delays in deliveries.
Risk: Misallocation of resources or overestimating the capacity to scale can create operational bottlenecks and financial instability.
4. Resistance to Change
Example: Blockbuster vs. Netflix
Blockbuster, the video rental giant, refused to pivot to a digital streaming model when Netflix emerged as a competitor. Blockbuster’s leadership failed to understand the long-term impact of the shift to online streaming and digital rentals, choosing instead to cling to its traditional brick-and-mortar business.
Risk: Internal resistance to change, even when clear signals point to a new direction, can result in a company’s failure to adapt to industry trends.
5. Implementation Challenges
Example: Windows Vista
Microsoft’s launch of Windows Vista in 2007 faced multiple execution problems, including compatibility issues with hardware, software, and a slow rollout. Despite the massive marketing effort, the operating system failed to gain traction, with users preferring Windows XP or waiting for the release of Windows 7.
Risk: Even with a well-planned strategy, poor execution and a lack of testing can lead to product failure and customer dissatisfaction.
6. Overconfidence and Biases
Example: Nokia’s Decline
Nokia, once a leader in mobile phones, was overconfident in its ability to maintain market dominance. It failed to recognize the shift to smartphones, especially with Apple’s iPhone and Google’s Android, leading to its fall from industry leadership.
Risk: Overestimating one’s position in the market and ignoring disruptive innovations can cause complacency, leading to a loss of competitive advantage.
7. Lack of Flexibility
Example: Blackberry
Blackberry, once the dominant smartphone brand known for its security and physical keyboard, failed to adapt to the growing demand for touchscreen smartphones and apps. By the time they introduced a touchscreen model, Apple and Android had already captured the market.
Risk: Failing to remain flexible and agile in response to new customer preferences and technological advances can leave a company vulnerable to disruption.
8. Financial Risks
Example: Enron’s Collapse
Enron’s leadership took massive financial risks, including using complex accounting practices (like Special Purpose Entities) to hide debt. The company’s strategic risk of pursuing aggressive financial growth and cutting ethical corners resulted in one of the largest corporate bankruptcies in history.
Risk: High financial risk, especially when it involves unethical practices or lack of transparency, can destroy both the company’s reputation and financial stability.
9. Stakeholder Management Risks
Example: Amazon and its Treatment of Workers
Amazon’s rapid expansion and aggressive cost-cutting strategies have led to controversies regarding the treatment of warehouse workers. Although the company focused on growth, it alienated key stakeholders (employees) through poor working conditions and low wages, which has sparked public backlash.
Risk: Ignoring the interests of key stakeholders, such as employees or customers, can lead to reputational damage and legal challenges.
10. Brand and Reputation Risks
Example: Pepsi’s Kendall Jenner Ad (2017)
Pepsi faced widespread backlash over an ad featuring Kendall Jenner, which was accused of trivializing social justice movements, particularly the Black Lives Matter protests. The ad was pulled after public outrage, damaging Pepsi’s brand image.
Risk: Misjudging cultural or social sensitivities can result in significant harm to a brand’s reputation, even with well-intended marketing efforts.
11. Strategic Drift
Example: Sears
Sears, once a dominant retail chain in the U.S., experienced strategic drift as it failed to respond to changing consumer shopping habits (e.g., the shift to e-commerce) and continued investing in a declining store model. By the time it attempted to change, it was too late to recover from years of underperformance.
Risk: Failing to adjust a strategy in response to market changes can lead to a gradual decline in competitiveness.
12. Legal and Ethical Risks
Example: Volkswagen Emissions Scandal (2015)
Volkswagen’s “Diesel gate” scandal, where it was found to have installed software in its diesel cars to cheat emissions tests, represents a major ethical and legal failure. The company’s strategy of cheating to meet regulatory standards ultimately led to billions in fines, lawsuits, and damage to its reputation.
Risk: Ethical lapses or illegal practices, even when they might seem strategically advantageous in the short term, can result in severe long-term consequences.
Conclusion
The risks of strategic management can feel overwhelming at times, but with the right mindset and tools, business leaders can turn these challenges into stepping stones for success. Whether it’s market volatility, internal resistance, or technological disruption, every risk presents an opportunity for growth and improvement.
By staying vigilant, remaining adaptable, and focusing on strategic execution, business leaders can not only mitigate risks but also set the stage for long-term success.
FAQ: Strategic Management Risks – Key Challenges for Business Leaders
1. What is strategic management, and why is it important?
Answer: It’s the process of formulating and executing strategies to achieve long-term goals, ensuring alignment, growth, and sustainability in a competitive market.
2. What are the common risks in strategic management?
Answer: Risks include unpredictable market conditions, lack of organizational vision, tech disruptions, poor execution, resistance to change, competition, and global events.
3. How can businesses mitigate market-related risks?
Answer: Diversify business models, stay flexible, and remain agile to adapt to market changes.
4. Why is a clear organizational vision important?
Answer: It aligns the team, reduces confusion, and ensures efficient resource use.
5. How can execution failures be avoided?
Answer: Invest in project management, monitor progress, and adjust plans as needed.
6. What’s the role of resistance to change in strategic management?
Answer: Resistance can slow down progress; businesses should manage change by involving employees and showing benefits.
7. How can companies stay ahead of competitors?
Answer: Monitor competitors regularly, innovate, and be proactive.
8. Examples of companies failing to manage strategic risks?
Answer: Kodak, Blockbuster, Nokia, Enron, Volkswagen all suffered from poor risk management.
9. How can businesses handle global risks?
Answer: Stay informed, build contingency plans, and diversify operations.
10. Why foster an innovative culture?
Answer: It allows companies to adapt to changes and stay competitive.

