Vendor Relationship Management: Moving Beyond Transactions to Strategic Partnerships

In modern enterprises, vendor relationship management is no longer a background procurement activity. As organizations enter 2026, vendors influence everything from regulatory exposure and operational continuity to product innovation and customer experience. A single weak vendor relationship can trigger compliance violations, service breakdowns, or reputational damage.
Vendor relationship management (VRM) is the discipline that helps businesses build structured, transparent, and value-driven partnerships with third parties. When executed well, VRM transforms vendors from cost centers into strategic contributors.
This article explains what vendor relationship management really means today, why it is critical for business resilience, and how companies can adopt practical, technology-enabled approaches to manage vendor risk, performance, and collaboration effectively.
What Is Vendor Relationship Management?
Vendor relationship management refers to the end-to-end approach organizations use to govern interactions with vendors throughout their lifecycle. This includes selection, onboarding, performance tracking, risk assessment, compliance oversight, and long-term relationship development.
Rather than focusing solely on price and delivery, VRM evaluates how vendors impact business objectives, regulatory obligations, and operational stability.
Vendor vs. Supplier: Why the Distinction Matters
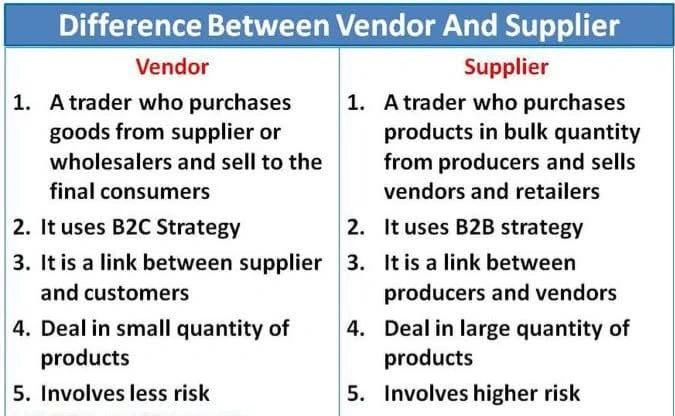
A supplier typically provides standardised goods or services with limited business dependency.
A vendor, however, often delivers specialised services, technology platforms, data processing, or regulated activities that directly affect business outcomes.
Vendor relationship management prioritises these high-impact relationships where failure or misalignment carries significant risk.
Traditional Vendor Management vs. Strategic Vendor Relationship Management
Traditional approaches emphasize contract enforcement and periodic reviews. Strategic VRM shifts the focus toward ongoing insight, shared accountability, and long-term value creation.
The difference lies not in managing vendors but in managing relationships.
Why Vendor Relationship Management Is a Strategic Business Priority
Vendor relationship management has moved into the boardroom because vendor-related risks are no longer isolated events.
Reducing Business and Compliance Risk
Strong VRM frameworks help organizations identify early warning signals such as financial instability, regulatory non-compliance, or operational weakness. This allows businesses to intervene before issues escalate into disruptions or penalties.
Strengthening Operational Reliability
When vendors are aligned with expectations and measured consistently, delivery becomes predictable. This improves service quality, reduces downtime, and minimizes costly rework.
Enabling Innovation Through Collaboration
Vendors that are treated as strategic partners are more likely to invest in joint problem-solving, process improvements, and innovation initiatives creating advantages competitors struggle to replicate.
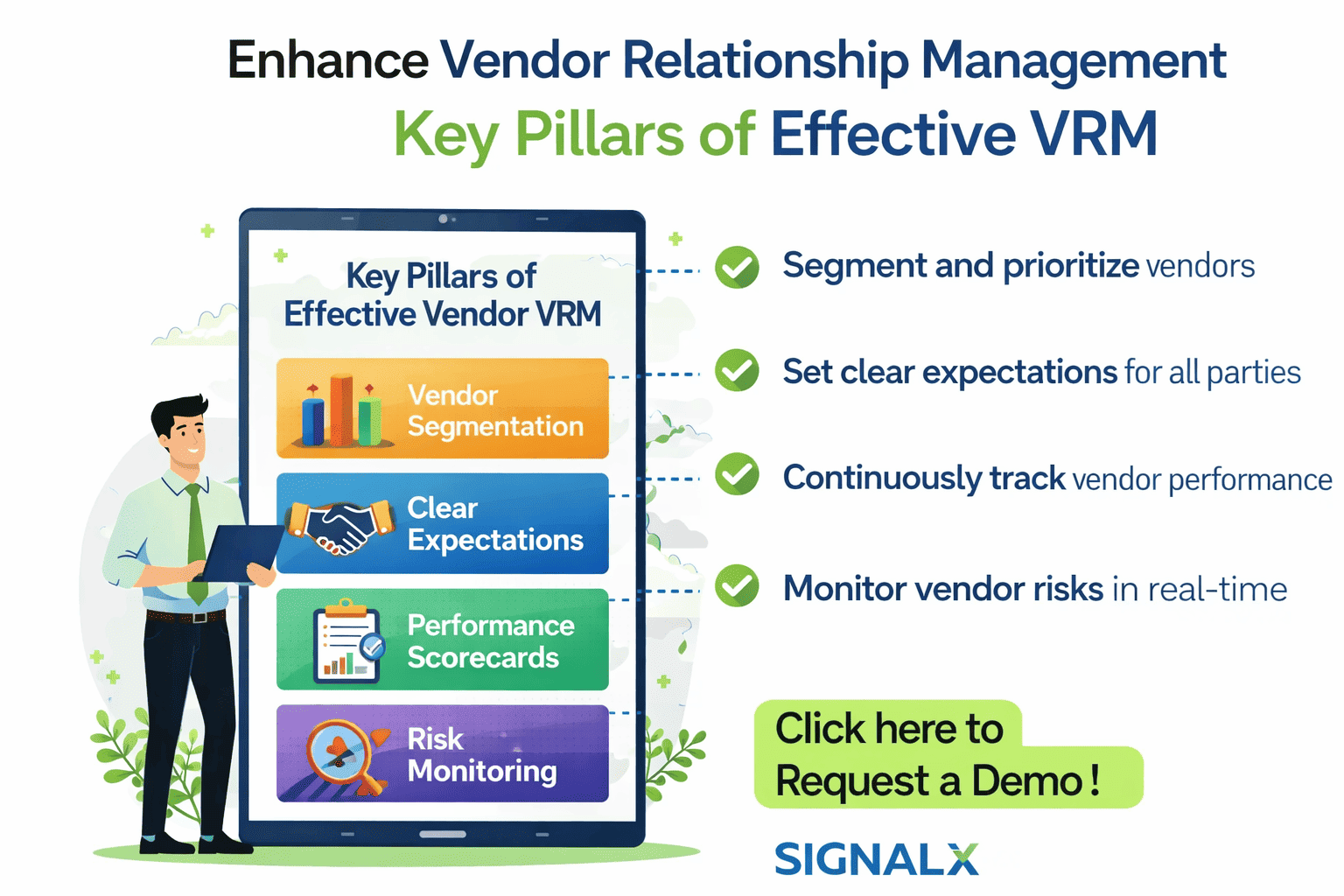
Key Pillars of Effective Vendor Relationship Management
Vendor Segmentation in Vendor Relationship Management
Not all vendors carry the same level of importance or risk. Effective VRM begins by grouping vendors based on factors such as:
- Business criticality
- Regulatory exposure
- Data sensitivity
- Financial and operational risk
- This ensures governance efforts are focused where they matter most.
Setting Clear Expectations and Accountability
Vendor relationship management depends on mutual clarity. This includes:
- Defined service levels
- Measurable performance indicators
- Transparent escalation processes
When expectations are documented and communicated clearly, trust increases and disputes decrease.
Performance Measurement and Scorecards
Vendor scorecards provide an objective view of performance over time. Common metrics include service reliability, turnaround time, compliance adherence, and issue resolution effectiveness.
Consistent measurement turns subjective opinions into actionable insights.
Continuous Risk Identification and Monitoring
Vendor risks are not static. Financial health, regulatory requirements, and external threats evolve continuously. Modern VRM requires ongoing monitoring rather than one-time assessments.
Contractual Structure and Governance Models
Contracts should support not hinder effective vendor relationship management. Governance models must define review cycles, ownership responsibilities, and remediation mechanisms across the contract lifecycle.
Collaboration and Joint Value Creation
The most mature VRM programs emphasize collaboration. Vendors are invited into planning discussions, improvement initiatives, and innovation efforts, creating shared ownership of outcomes.
Best Practices for Strong Vendor Relationship Management
Organizations that excel in vendor relationship management consistently apply the following practices:
- Conduct structured relationship and performance reviews
- Align vendors to broader business objectives
- Encourage two-way feedback and transparency
- Use data to guide decisions instead of assumptions
- Maintain executive sponsorship for critical vendors
These practices turn vendor interactions into long-term partnerships rather than transactional exchanges.
The Role of Technology in Modern Vendor Relationship Management
Why Manual Approaches No Longer Work
Spreadsheets and email-based tracking fail to provide real-time visibility into vendor performance and risk. They often lead to inconsistent data, delayed responses, and fragmented accountability.
How Technology Enhances Vendor Relationship Management
Digital VRM platforms enable organizations to:
- Centralize vendor data
- Automate performance evaluations
- Monitor risks continuously
- Generate insights for faster decision-making
Technology shifts VRM from reactive administration to proactive intelligence.
How SignalX Supports Advanced Vendor Relationship Management
SignalX strengthens vendor relationship management by embedding intelligence and automation into vendor oversight.
AI-Powered Vendor Risk Intelligence
SignalX analyzes multiple data signals to identify emerging vendor risks. This enables organizations to detect financial stress, compliance gaps, or operational red flags before they impact the business.
Streamlined Vendor Due Diligence
SignalX provides structured workflows for vendor onboarding and evaluation. This reduces manual effort while improving consistency, governance, and speed.
Ongoing Regulatory and Compliance Oversight
For organizations operating in regulated environments, SignalX supports continuous monitoring aligned with Indian regulatory expectations such as RBI and SEBI frameworks.
Centralized Visibility for Leadership Teams
SignalX dashboards consolidate vendor performance and risk metrics into a single view, empowering leaders to make informed, timely decisions.
Ready to Transform Your Vendor Relationship Management?
Move beyond transactional vendor oversight and gain real-time visibility into vendor performance,
risk, and compliance. SignalX helps you build resilient, compliant, and intelligence-driven vendor
relationships.
Contact Us
Practical Vendor Relationship Management Checklist
✔ Identify and categorize critical vendors
✔ Define measurable performance and risk indicators
✔ Establish governance and review schedules
✔ Monitor vendor risk continuously
✔ Use technology to centralize insights
✔ Document corrective actions and follow-ups
Common Vendor Relationship Management Challenges and Solutions
Lack of Transparency
→ Introduce standardized reporting and dashboards
Misaligned Expectations
→ Formalize KPIs and communication structures
Fragmented Ownership
→ Assign clear internal accountability
Reactive Risk Management
→ Adopt continuous monitoring and intelligence tools
The Future of Vendor Relationship Management
Vendor relationship management has evolved into a strategic capability that directly influences business continuity, compliance, and growth. Organizations that invest in structured VRM frameworks and intelligent tools are better equipped to manage uncertainty and unlock long-term value from their vendor ecosystems.
Moving from transactional oversight to transformational partnerships is no longer optional it is a competitive necessity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes vendor relationship management different from vendor management?
Vendor relationship management focuses on long-term value, collaboration, and risk governance, rather than just contracts and costs.
How frequently should vendors be evaluated?
High-risk or business-critical vendors should be monitored continuously, with formal reviews conducted quarterly.
Which metrics are most important in vendor relationship management?
Performance reliability, compliance adherence, risk indicators, and issue resolution effectiveness.
How does signal intelligence improve vendor decisions?
Signal intelligence provides early visibility into emerging risks, allowing proactive action rather than reactive response.